B4. Income taxes
AP ACCOUNTING PRINCIPLES
The Group’s tax expense comprises current tax and deferred tax.
Current tax is calculated on the taxable profit for the period based on the tax rules prevailing in the countries where the Group operates. Since taxable profit excludes costs that are not tax deductible and income that is not taxable, this is differentiated from profit before tax in profit or loss. Current tax also includes adjustments relating to recognized current tax from prior periods. Interest attributable to income tax and withholding taxes deducted at source on intra-Group transactions are also recognized as income tax.
Deferred tax is calculated based on temporary differences between the carrying amounts and the taxable values of assets and liabilities and for tax loss carryforwards in so far as it is probable that these can be utilized against future taxable profits. Deferred taxes are measured at their nominal amount and based on the tax rates enacted or substantively enacted on the balance sheet date. Deferred tax is not calculated on the initial recognition of goodwill or when an asset or liability is recognized for the first time, provided that the asset or liability is not attributable to an acquisition. SCA does not recognize tax that may arise on future dividends of the retained earnings of foreign subsidiaries. Any such future effects (withholding tax deducted at source and other deferred tax on profit-taking within the Group) are recognized when SCA can no longer control the reversal of such differences or when, for other reasons, it is probable that a reversal can take place in the foreseeable future.
The recognition of tax effects is determined by the manner in which the underlying transaction is recognized. For items in profit or loss, the tax effect is recognized in profit or loss. For transactions in equity and in other comprehensive income, the tax effect is recognized in equity and in other comprehensive income, respectively.
Tax liabilities and tax assets are recognized net when SCA has a legal right to offset.
KAA KEY ASSESSMENTS AND ASSUMPTIONS
For companies that operate globally and thus apply significantly different taxation legislation, determining deferred tax assets and tax liabilities is complicated. This requires that assessments and assumptions be made to determine the value of the deferred tax asset and deferred tax liability on the balance sheet date. Future changes to taxation legislation and trends in the business climate will impact the company’s future taxable profits and thus its possibility to utilize deferred tax assets on loss carryforwards and other temporary differences. As of December 31, 2016, SEK 1,465m was recognized as deferred tax assets based on best assessment of future taxable profits in the Group. At year-end 2016, the Group also had taxable losses of SEK 4,687m, for which no deferred tax asset had been recognized. Accordingly, a changed assessment of the probability of future taxable profits could have a positive or negative effect.
Key assessments and assumptions are also made regarding recognition of provisions and contingent liabilities relating to tax risks. For further information, see Note D7 and Note G3.
Tax expense
SEKm |
2016 |
% |
2015 |
% |
2014 |
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current tax |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income tax for the period |
2,872 |
27.7 |
2,019 |
20.2 |
2,145 |
22.6 |
Adjustments for prior periods |
1,656 |
16.0 |
–2 |
–0.0 |
–155 |
–1.6 |
Current tax expense |
4,528 |
43.7 |
2,017 |
20.2 |
1,990 |
21.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deferred tax |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Changes in temporary differences |
–46 |
–0.4 |
323 |
3.2 |
472 |
5.0 |
Adjustments for prior periods |
–419 |
–4.1 |
349 |
3.5 |
97 |
1.0 |
Revaluation |
285 |
2.8 |
–149 |
–1.5 |
–139 |
–1.5 |
TB4:2 Deferred tax expense |
–180 |
–1.7 |
523 |
5.2 |
430 |
4.5 |
IS Tax expense |
4,348 |
42.0 |
2,540 |
25.4 |
2,420 |
25.5 |
Explanation of tax expense
The difference between the recognized tax expense and expected tax expense is explained below. The expected tax expense is calculated based on profit before tax in each country multiplied by the tax rate in effect in the country.
SEKm |
2016 |
% |
2015 |
% |
2014 |
% |
||||||
|
||||||||||||
IS Profit before tax |
10,360 |
|
9,992 |
|
9,488 |
|
||||||
IS Tax expense |
4,348 |
42.0 |
2,540 |
25.4 |
2,420 |
25.5 |
||||||
Expected tax expense |
2,258 |
21.8 |
2,267 |
22.7 |
2,251 |
23.7 |
||||||
Difference |
2,090 |
20.2 |
273 |
2.7 |
169 |
1.8 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
The difference is explained by: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Permanent differences between accounting and taxable result |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Effects of subsidiary financing |
–152 |
–1.5 |
–71 |
–0.7 |
–21 |
–0.2 |
||||||
Effects of acquisitions and divestments |
27 |
0.3 |
–23 |
–0.2 |
99 |
1.0 |
||||||
Taxes relating to profit-taking in the Group |
37 |
0.4 |
27 |
0.3 |
9 |
0.1 |
||||||
Other permanent effects 1) |
377 |
3.6 |
17 |
0.2 |
176 |
1.9 |
||||||
Taxes related to prior periods 2) |
1,237 |
12.0 |
347 |
3.4 |
–58 |
–0.6 |
||||||
Changes in the value of deferred tax assets 3) |
668 |
6.4 |
23 |
0.2 |
–76 |
–0.8 |
||||||
Changes in tax rates |
–104 |
–1.0 |
–47 |
–0.5 |
40 |
0.4 |
||||||
Total |
2,090 |
20.2 |
273 |
2.7 |
169 |
1.8 |
||||||
Current tax liability
SEKm |
2016 |
2015 |
2014 |
Value, January 1 |
–45 |
95 |
283 |
Current tax expense |
4,528 |
2,017 |
1,990 |
CF TB4:1 Paid tax |
–3,799 |
–2,208 |
–2,101 |
Other changes from aquisitions, divestments and reclassifications |
–487 |
13 |
–111 |
Translation differences |
–3 |
38 |
34 |
Value, December 31 |
194 |
–45 |
95 |
BS of which current tax liability |
935 |
827 |
747 |
BS of which current tax asset |
741 |
872 |
652 |
TB4:1 Paid tax
SEKm |
2016 |
2015 |
2014 |
Country |
|
|
|
Sweden |
–1,313 |
–79 |
–65 |
Germany |
–516 |
–358 |
–271 |
Spain |
–405 |
–90 |
–90 |
Netherlands |
–215 |
–59 |
–191 |
China |
–146 |
–236 |
–51 |
Belgium |
–144 |
–80 |
–91 |
UK |
–136 |
–115 |
–92 |
Austria |
–94 |
–100 |
–60 |
Italy |
–94 |
–87 |
–77 |
Mexico |
–88 |
–121 |
–107 |
Colombia |
–83 |
–72 |
–179 |
Ecuador |
–67 |
–41 |
–21 |
Russia |
–64 |
–59 |
–81 |
Slovakia |
–61 |
–30 |
–39 |
Japan |
–57 |
–35 |
–45 |
Denmark |
–40 |
–26 |
–36 |
Finland |
–37 |
–48 |
–8 |
Norway |
–30 |
–41 |
–34 |
Costa Rica |
–26 |
–14 |
–12 |
Poland |
–26 |
–2 |
–26 |
Other countries |
–157 |
–515 |
–525 |
CF Total |
–3,799 |
–2,208 |
–2,101 |
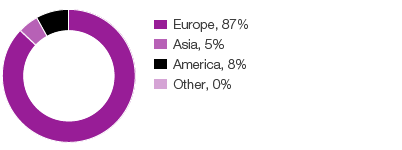
Paid tax by region 2016, % of Group
TB4:2 Deferred tax liability
SEKm |
Value, January 1 |
Deferred tax expense |
Other changes 2) |
Translation differences |
Value, December 31 |
||||
|
|||||||||
Intangible fixed assets |
1,435 |
89 |
85 |
70 |
1,679 |
||||
Property, plant and equipment |
11,437 |
–234 |
524 |
285 |
12,012 |
||||
Financial non-current assets |
–89 |
180 |
–52 |
8 |
47 |
||||
Current assets |
–260 |
–42 |
20 |
–6 |
–288 |
||||
Provisions |
–497 |
–386 |
–127 |
–53 |
–1,063 |
||||
Liabilities |
–655 |
–290 |
367 |
–28 |
–606 |
||||
Tax credits and tax loss carryforwards |
–1,405 |
526 |
–541 |
–69 |
–1,489 |
||||
Other |
47 |
–23 |
–66 |
3 |
–39 |
||||
BS Total 1) |
10,013 |
–180 |
210 |
210 |
10,253 |
||||
Loss carryforwards
Future tax credit and loss carryforwards for which deferred tax assets were recognized have been reported at the tax amount of SEK 1,489m in TB4:2.
Loss carryforwards for which no deferred tax assets were recognized amounted to SEK 4,687m (2,649; 2,644) gross at December 31, 2016. The expiry dates of these loss carryforwards are distributed as follows.
The change in uncapitalized loss carryforwards for the period includes SEK 85m that has expired and SEK 64m that was either utilized or capitalized. The tax value of uncapitalized tax loss carryforwards amounted to SEK 1,382m (779; 812).
Year of maturity |
SEKm |
2017 |
85 |
2018 |
917 |
2019 |
1 |
2020 |
1 |
2021 and later |
1,001 |
Indefinite life |
2,682 |
Total |
4,687 |
